
Learn more about a clinical trial designed to evaluate an investigational study medication in adults living with elevated liver fat and obesity or overweight.

Learn more about a clinical trial designed to evaluate an investigational study medication in adults living with elevated liver fat and obesity or overweight.

This clinical trial will help us learn if an updated COVID-19 vaccine is safe, and if it can help the immune system defend against new variants of the virus in healthy adults who do not have risk factors for severe COVID-19.

GZP2 is a clinical research study from Eli Lilly and Company. It is testing if an investigational medicine (a medicine being studied) can safely help people with obesity or overweight

GZP1 is a clinical research study from Eli Lilly and Company. It is testing if an investigational medicine (a medicine being studied) can safely help people with obesity or overweight with at least 1 weight-related health condition, reduce their body weight.
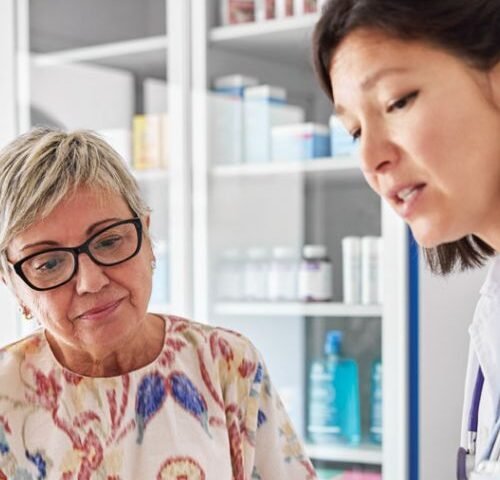

C. difficile (C. diff) is a contagious bacteria (germ) that infects the colon (large intestine) and can cause diarrhea and other health complications.
Are you interested in contributing to research on COVID-19 vaccines? We are conducting a clinical study evaluating an investigational vaccine that may help protect against the Omicron JN.1 subvariant of COVID-19.
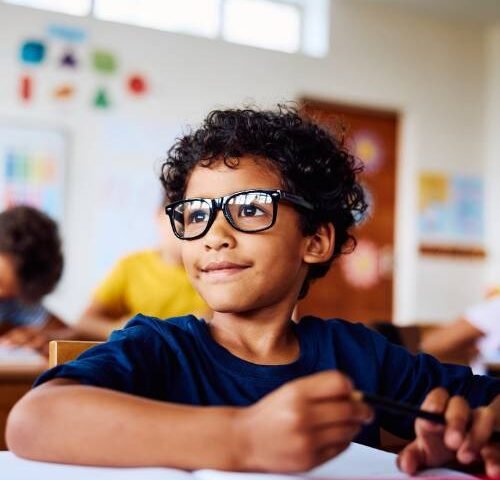

Introducing an updated COVID-19 vaccine clinical trial for children 5 to 11 years of age who are at increased risk of severe illness.
Please take one to learn more.
Who can take part
This clinical trial may be an option for children who are [5 to 11 years] of age and:
Have at least 1 medical condition that increases their risk of severe COVID-19, such as:
-Have not been diagnosed with COVID-19 recently
-Have not received a COVID-19 vaccine recently
-Do not have a history of severe allergic reactions associated with any vaccine
There are other requirements that the study team will discuss with you.
What to expect
If this study is a good fit for your child and you agree to have them take part, here is what you can expect:
Study vaccine
Your child will receive 1 dose of the study vaccine as an injection (shot) in the upper arm.
Study duration
Participation lasts about [6] months and includes at least [2] in-person visits and [1] phone call.
Study-related costs
There is no cost to participate. [You will also be reimbursed for study-related expenses.]
Participation in this clinical trial is completely voluntary. Your child can leave the study at any time, for any reason.
About the study vaccine
The study vaccine is a modified version of Pfizer-BioNTech’s original mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine. The updated formulation is designed to improve protection against the latest circulating variant of the COVID-19 virus recommended by
the [US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and] World Health Organization (WHO) for 2025- 2026 vaccines. It is currently approved for use in individuals 5 to 64 years of age with at least one underlying condition that puts them at risk of
severe outcomes from COVID-19.
Your child’s safety is the top priority. Before joining the study, you will be given all of the details about participation, including potential benefits and risks. Your child’s health will be carefully monitored through the clinical trial by the study team.
Staying up to date on your child’s COVID-19 vaccines is still the best way to prevent serious illness. However, as the virus continues to change, vaccines must be updated as well.
This study will help us learn if an updated COVID-19 vaccine is safe, and if it can help the immune system defend against new variants of the virus in children 5 to 11 years of age who are at increased risk of severe illness.
By participating in this clinical trial, your child will receive a COVID-19 vaccine that may reduce their risk of severe illness while contributing to research that could help protect millions of others around the world. So, thank you for taking the time to learn more.
Tomorrow’s breakthroughs start today with you
Participation by families of all backgrounds is critical to developing vaccines that protect children against the latest variants of COVID-19, including those who are most at-risk. Every new vaccine breakthrough helps us reach more communities to prevent and reduce the spread of disease.
Ready to learn more?
For more information, contact our study team 786-772-0510

The BeyondCOVE Trial is doing further research on 2 approved COVID-19 vaccines to learn more about how well the vaccines can protect against COVID-19 illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its multiple variants.
The trial will last about 6 months and has 2 trial visits and 2 phone call check-ins. All participants will receive 1 injection.
To join the trial, you must:
There are additional requirements, which the trial team can explain to you.
To learn more about this trial, please contact the clinical trial site listed here:
786-772-0510
Diseases do not discriminate — and neither should clinical trials. Moderna is committed to researching safe and effective mRNA-based vaccines and therapies to bring better health and living to people of all ages, sexes, and backgrounds.

Are you interested in participating in this clinical study?
Double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose selection study in adults to assess the safety and immunogenicity of vaccines.
Inclusion criteria:
Written informed consent obtained from the participant prior to performing any protocol-related procedures.
Body mass index (BMI) < 35 kg/m² at screening.
Learn more:
Call us 786-772-0510

If menstrual migraines are cramping your style, it’s time to let your voice be heard by others who understand. By participating in clinical research, you can help advance understanding of menstrual migraine.